Diamonds Buying Guide
| This natural stone is a popular gemstone especially for engagement rings and earrings. Before you buy diamonds, you should understand the four standard measurements: cut, carat, colour and clarity. These measurements are used to compare and grade diamonds and will help you decide what type to buy based on your budget and style preferences. |
| |
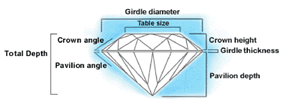
CUT AND SHAPEThe cut refers to the shape of the diamond, based on the angles and proportions that allow light to reflect from one facet to another. Diamond shapes are many and varied, ranging from round cuts and hearts to pear and oval. The traditional shape is round brilliant with 58 facets as its symmetry allows it to reflect more light, making it the most brilliant of all the shapes. The famous Tiffany diamond was given 90 facets, 32 more than the traditional round brilliant cut, giving the Tiffany diamond intense colour and brilliance. Other popular shapes are marquise, emerald and princess.
Diamonds are known for their brilliance and a well-cut diamond should maximise this effect, whether it’s solitaire (a jewel set by itself) or in a gold or platinum setting. The cut of a diamond consists of three factors: grade, depth and polish.
| |
Back to top | |
| |
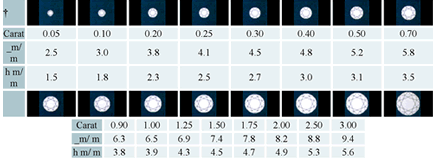
CARAT1 carat = 100 points = 200 milligrams (one fifth of a gram) The cut and setting can often make a diamond look bigger than its carat weight so examine all 4 standard measurements before buying. Large diamonds are quite rare and naturally, prices increase significantly with the carat weight. If you want a high carat diamond, often the case when buying an engagement ring, consider a slight downgrade in size.
| |
Back to top | |
| |
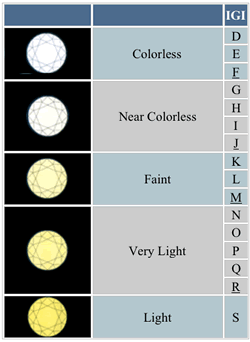
COLOURAll diamonds possess trace amounts of yellow or brown – the most valuable diamonds tend to be the colourless diamonds. However, very deeply coloured diamonds, such as a brilliant canary yellow diamond, can actually cost more than a colourless stone. These ‘fancy diamonds’ (also called Z+ diamonds) are even rarer than their colourless counterparts, and can also be found in blue, green, black, red and pink. The most famous fancy diamond is the deep yellow Tiffany diamond. Another famous gem is the Millennium diamond, the world’s largest 'D colour' diamond for its virtual flawlessness. The chart below explains the grading of diamond colours from D to Z. Colourless diamonds are graded D and are very rare. The colour of a diamond can affect the setting in engagement rings. White colours are often set in white gold or platinum while the warmer tones are often set yellow gold.
| |
Back to top | |
| |
CLARITYThe majority of diamonds have inclusions (small mineral traces or flaws), which are often undetectable to the naked eye and devalue the stone. The number of inclusions, their size and where they are located on the diamond can also affect the flow of light through a diamond, which reduces the brilliance. Flawless diamonds are uncommon and therefore very expensive. However, many inclusions can be concealed by a setting, which is frequently used for diamond rings. eBay sellers often describe the clarity of larger, solitaire diamonds by referring to the industry letter grading scale. Diamonds with inclusions visible to the naked eye have a grading of I1 - I3. Small inclusions have a grading of SI1 - SI2 while diamonds with very small inclusions have a grading of VS1 - VS2. Diamonds with even tinier inclusions are graded VVS1 - VVS2 while rare diamonds with no inclusions are either known as flawless (FL) or internally flawless (IF). The International Gemological Institute (IGI) uses the grading scale below for clarity.
| |
Back to top | |
| |
CERTIFICATIONMany eBay diamond sellers offer certificated listings that include diamond appraisal (estimated retail value) and certification value in their listings. Certification, (official documents issued by third-party gemological labs) states the details about each gem (as a minimum, a grading report of the 4 Cs - cut, carat, colour and clarity) and is independent of market value. The certification can also include:
Before you buy a diamond on eBay:
| |
Back to top | |
| |
OTHER DIAMONDS AND CRYSTALSThere are many manufactured diamonds on the market which include pink, blue and black diamonds and even colourless diamonds which have been clarity-enhanced. These are some of the enhanced stones you may come across: Also available are a range of diamond look-alikes: | |
Back to top | |
| |
MAINTENANCEDiamonds might be the hardest naturally-occurring substance on Earth, but they need to be looked after. Diamonds, loose or otherwise, should be stored individually in soft cloth pouches to prevent the stones from hitting each other and chipping. Certain settings also offer better protection: four-prong setting, six-prong setting and low-profile channel (also known as bezel settings). Regular Cleaning Diamonds are renowned for their brilliance, but dust, oil from your skin and other unclean substances can reduce the stone’s sparkle. To protect your diamond ring, engagement ring and earrings, follow the tips below and remember, if the diamond is in a metal setting, treat it gently as gold can scratch.
Professional Maintenance Jewellers can also clean diamonds and gems for you, using steam or ultrasound. However, ultrasound can aggravate internal fissures or flaws so make sure the diamond’s existing clarity isn’t affected. You should also ask the jeweller to ensure the diamonds are secure in their settings to prevent the stones from falling out. | |
Back to top | |
| Content Provided By | |
| Shop on eBay | |
| Resources | |||||
|